(2022.3 Kagoshima University)
Updated on 2026/02/06
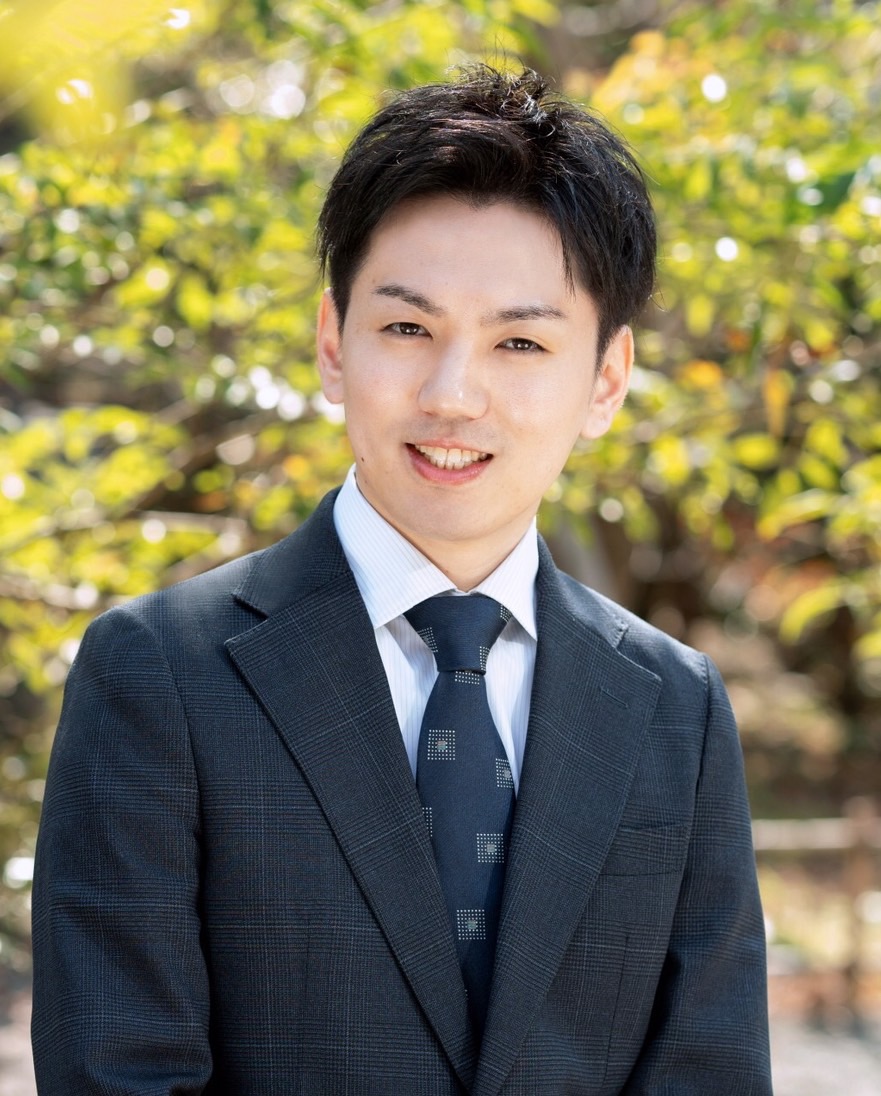

occupational health
gerontology
2025.4 日本基礎理学療法学会 researchmap
2023.4 Japanese Society of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention researchmap
2023.4 鹿児島県理学療法士協会 researchmap
2023.2 日本予防理学療法学会 researchmap
2022.12 日本産業理学療法研究会 researchmap
2022.2 International Federation of Physiotherapists working in Occupational Health and Ergonomics (IFPOHE) researchmap
2021.11 Japan Geriatric Therapy Society researchmap
2020.11 Japan Geriatrics Society researchmap
2020.9 Japanese Association on Sarcopenia and Frailty researchmap
2018.4 日本腎臓リハビリテーション学会 researchmap
2018.4 Japanese Society of Physical Therapy researchmap
2018.4 World Physiotherapy researchmap
2018.4 - 2023.3 熊本県理学療法士協会 researchmap
2023.4 AMED. サルコペニア・フレイルの予防に関するヘルスケアサービスのためのガイドライン開発研究 研究参加者
2021.6 - 2022.2 熊本県理学療法士学会 第24回熊本県理学療法士学会 準備委員 Academic society
2020.5 - 2020.10 日本地域理学療法学会 COVID-19特別チーム
2020.5 - 2020.10 日本予防理学療法学会 社会的制約改善班
白土 大成 . 知っておきたい・深めたい Close-up 遠隔理学療法 フレイル・サルコペニアに対する遠隔理学療法の現状 . 理学療法ジャーナル59 ( 12 ) 1462 - 1465 2025.12
Shiratsuchi D, Miyake Y, Kuratsu R, Nishi H, Fukumori M, Atae S, Kiyama R, Kosakamoto R, Tanaka H, Makizako H . Is psychological engagement more important than participation? Volunteer activity and subjective cognitive function in older adults. . Aging clinical and experimental research37 ( 1 ) 332 2025.11
Shiratsuchi D, Makizako H, Akaida S, Miyake Y, Kiyama R, Tabira T, Tateishi M, Otsuka R, Takenaka T, Kubozono T, Ohishi M . Combinations of intrinsic capacity and frailty and their associations with self-rated health in community-dwelling older adults. . Aging clinical and experimental research37 ( 1 ) 275 2025.9
Kento Muto, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Masataka Nagai, Masafumi Kubota . Differences in factors associated with stair-climbing ability at discharge based on the severity of lower limb paralysis in patients with stroke . Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation32 ( 8 ) 1 - 8 2025.5Reviewed
Shiratsuchi Daijo, Makizako Hyuma, Akaida Shoma, Tateishi Mana, Taniguchi Yoshiaki, Takenaka Toshihiro, Kubozono Takuro, Ohishi Mitsuru . Association of metabolic syndrome and low physical function with mild cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional analysis from the Tarumizu Study . Japanese Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention60 ( 1 ) 36 - 43 2025.2
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 . 高齢者におけるメタボリックシンドロームおよび身体機能低下と軽度認知障害との関連 垂水研究による横断分析 . 日本循環器病予防学会誌60 ( 1 ) 36 - 43 2025.2
Akaida S, Tabira T, Tateishi M, Shiratsuchi D, Shimokihara S, Kuratsu R, Akasaki Y, Hidaka Y, Makizako H . Averting older adults' memory function decline via meaningful activities: a follow-up longitudinal study. . European geriatric medicine15 ( 6 ) 1793 - 1801 2024.12
Shiratsuchi D, Taniguchi Y, Kiuchi Y, Akaida S, Makizako H . Association of alpha-actinin-3 genotype with muscle mass and physical function in community-dwelling older adults. . European geriatric medicine16 ( 1 ) 15 - 22 2024.10
立石 麻奈, 赤井田 将真, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . フレイル高齢者に対する個別運動と集団運動による効果の相違の検証 ランダム化比較試験 . 日本老年医学会雑誌61 ( 4 ) 447 - 455 2024.10
Akaida S, Makizako H, Tateishi M, Shiratsuchi D, Taniguchi Y, Kiuchi Y, Kiyama R, Takenaka T, Kubozono T, Ohishi M . Importance of Lifestyle Activities for Older Adults' Psychosomatic Functions After Driving Cessation: Interpretation by a Mixed-Methods Study. . Journal of applied gerontology : the official journal of the Southern Gerontological Society44 ( 4 ) 7334648241277043 - 541 2024.9
Makizako H, Akaida S, Shiratsuchi D, Tateishi M . Are Middle-Aged and Older Adult Users of Physical Activity Monitoring Systems More Physically Active and at a Lower Risk of Locomotive Syndrome? A Cross-Sectional Web-Based Online Survey. . Annals of geriatric medicine and research28 ( 3 ) 323 - 329 2024.9
Akaida S., Shiratsuchi D., Tateishi M., Kuratsu R., Makizako H. . Life satisfaction and awareness of meaningful activities among middle-aged adults: A population-based study . British Journal of Occupational Therapy87 ( 9 ) 556 - 563 2024.9
古谷 直弘, 四宮 明宏, 白土 大成, 土方 麻衣, 坂本 勇斗, 武藤 健人, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . 胃癌・大腸癌患者における術前のPossible Sarcopeniaと術後の合併症および在院日数との関連 後ろ向き観察研究 . 日本がん・リンパ浮腫理学療法学会誌2 39 - 47 2024.9
Abe Takafumi, Okuyama Kenta, Motohiro Atsushi, Shiratsuchi Daijo, Isomura Minoru . Association between different types of physical activity and occupational stress in Japanese workers: a cross-sectional study(タイトル和訳中) . Industrial Health62 ( 4 ) 227 - 236 2024.7
三宅 悠斗, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . 地域在住高齢者における睡眠の質と身体機能との関連性 共分散構造分析による介在する要因の検討 . 日本老年療法学会誌3 jgts.2023_017_OA - jgts.2023_017_OA 2024.3
Association between Preoperative Possible Sarcopenia Related Postoperative Complications and Length of Hospital Stay in Patients with Gastric and Colorectal Cancer . Japanese Journal of Physical Therapy for Oncology and Lymphedema2 ( 0 ) 39 - 47 2024
Abe T, Okuyama K, Motohiro A, Shiratsuchi D, Isomura M . Combined associations of regular exercise and work-related moderate-to-vigorous physical activity with occupational stress responses: a cross-sectional study. . Frontiers in sports and active living6 1386775 2024
Shiratsuchi D, Motohiro A, Okuyama K, Abe T . Relationship between occupational stress and presenteeism status among workers in small and medium-sized enterprises. . Archives of environmental & occupational health79 ( 2 ) 83 - 90 2024
白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . 【COVID-19とフレイルの実際】COVID-19とフレイルの実際 フレイルの社会的側面 . 日本老年医学会雑誌60 ( 2 ) 127 - 134 2023.4
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 生野 佐紀, 椎葉 竜平, 谷口 善昭, 富岡 一俊, 佐藤 菜々, 和田 あゆみ, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 中井 雄貴 . 新型コロナウイルス感染症の流行に伴う就労者の腰痛変化とプレゼンティーズムとの関連 . 理学療法学49 ( 5 ) 339 - 347 2022.10
Akaida Shoma, Nakai Yuki, Shiratsuchi Daijo, Tomioka Kazutoshi, Taniguchi Yoshiaki, Sato Nana, Wada Ayumi, Kiuchi Yuto, Shono Saki, Shiiba Ryuhei, Tateishi Mana, Makizako Hyuma . COVID-19緊急事態宣言下での地域在住日本人超高齢者の社会的交流の種類・頻度と自己評価健康度との関連(Association of self-rated health with type and frequency of social interaction during the declaration of COVID-19 state of emergency among Japanese community-dwelling oldest-old adults) . Geriatrics & Gerontology International22 ( 5 ) 405 - 411 2022.5
牧迫 飛雄馬, 白土 大成, 椎葉 竜平, 谷口 善昭, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 . 地域在住高齢者における運動器疾患、転倒歴および多剤併用とサルコペニアとの関連 . 日本予防理学療法学会雑誌1 19 - 24 2022.3
白土 大成, 椎葉 竜平, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . 【疾患別にみたサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際】運動器疾患患者のサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際 . 理学療法38 ( 11 ) 988 - 995 2021.11
福原 みなみ, 橋本 幸成, 白土 大成, 高野 文音 . 後方病変型他人の手徴候を呈した1症例 症状出現に関与した要因の検討 . 日本作業療法学会抄録集55回 OA - 12 2021.9
Makizako Hyuma, Nakai Yuki, Shiratsuchi Daijo, Akanuma Tomomi, Yokoyama Kaori, Matsuzaki-Kihara Yuriko, Yoshida Hiroto . COVID-19緊急事態宣言下での日本人後期高齢者における体力低下および認知機能低下の認識(Perceived declining physical and cognitive fitness during the COVID-19 state of emergency among community-dwelling Japanese old-old adults) . Geriatrics & Gerontology International21 ( 4 ) 364 - 369 2021.4
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Kento Tabira, Yuto Miyake, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi . Comparative associations of height- and body mass index-adjusted muscle mass with sarcopenia under the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia 2025 consensus . Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2026.4Reviewed
Yurika Tamekuni, Kenta Okuyama, Atsushi Motohiro, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Minoru Isomura, Linda Abrahamsson, Martin Lindström, Kristina Sundquist, Takafumi Abe . Physical and Social Factors Differentiating Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Among Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprise Workers in Japan: A Cross-Sectional Study . European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 2026.1Reviewed
三宅悠斗, 白土大成, 田平健人, 牧迫飛雄馬 . 地域在住高齢者における起立動作時の床反力と1年後の転倒および転倒恐怖感との関連 . 日本転倒予防学会誌 2026.1Reviewed
伊香孝則, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 三宅悠斗, 立石麻奈, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬 . 一過性のバーチャルリアリティ運動が実行機能と脳血流変化に与える影響 . 理学療法かごしま 2026.1Reviewed
Tsuge T., Yamamoto N., Tomita Y., Hagiyama A., Shiratsuchi D., Okamura M., Kaneko T., Suzuki K., Nakashima Y., Taito S., Yorifuji T. . Spin in systematic reviews of rehabilitation journals was high prevalence: Meta-epidemiological study . Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2025.12Reviewed
Shiratsuchi D., Miyake Y., Kuratsu R., Nishi H., Fukumori M., Atae S., Kiyama R., Kosakamoto R., Tanaka H., Makizako H. . Is Psychological Engagement More Important than Participation? Volunteer Activity and Subjective Cognitive Function in Older Adults . Aging Clin Exp Res 2025.12Reviewed
Takahiro Tsuge, Norio Yamamoto, Yosuke Tomita, Akikazu Hagiyama, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Masatsugu Okamura, Takao Kaneko, Kosuke Suzuki, Yuki Nakashima, Shunsuke Taito, Takashi Yorifuji . Association of Use of GRADE, Protocol Registration, and Journal Impact Factor With Reporting and Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews Published in Rehabilitation Journals: A Meta-Epidemiological Study . Cureus17 ( 10 ) e95695 2025.10Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchia, Hyuma Makizakoa, Shoma Akaidab,c, Yuto Miyakea, Ryoji Kiyamaa, Takayuki Tabirae, Mana Tateishif, Rei Otsukaf, Toshihiro Takenakag, Takuro Kubozonoh, Mitsuru Ohishih . Combinations of intrinsic capacity and frailty and their associations with self-rated health in community-dwelling older adults . Aging Clin Exp Res 2025.9Reviewed
Takahiro Tsuge, Norio Yamamoto, Yosuke Tomita, Akikazu Hagiyama, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yukiko Kato, Shunsuke Taito, Takashi Yorifuji . Reporting and Methodological Qualities of Systematic Reviews in Rehabilitation Journals After 2020: A Cross-sectional Meta-Epidemiological Study . Physical Therapy105 ( 4 ) 2025.3Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Keisuke Maeda, Katsuya Iijima, Hiroyuki Shimada, Tatsuro Inoue, Minoru Yamada, Ryo Momosaki, Hidetaka Wakabayashi, Koichi Yamamoto, Hidenori Arai . Effects of digital-based interventions on the outcomes of the eligibility criteria for sarcopenia in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Ageing Research Reviews104 102663 - 102663 2025.1Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Yuto Kiuchi, Ryota Kuratsu, Hyuma Makizako . Influence of exercise and dietary habits on the association of alpha‐actinin‐3 gene polymorphisms with physical function and body composition in community‐dwelling individuals aged 60 years and older . Geriatrics & Gerontology International25 ( 2 ) 173 - 181 2024.12Reviewed
Mana Tateishi, Shoma Akaida, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako . The difference in effect between individual exercise and collective exercise in older adults with frailty-A randomized controlled trial- . Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Geriatrics61 ( 4 ) 447 - 455 2024.10Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Shoma Akaida, Hyuma Makizako . Association of alpha-actinin-3 genotype with muscle mass and physical function in community-dwelling older adults . European Geriatric Medicine 2024.10Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Shoma Akaida, Hyuma Makizako . Association of alpha-actinin-3 genotype with muscle mass and physical function in community-dwelling older adults . European Geriatric Medicine 2024.10Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako;Shoma Akaida;Mana Tateishi;Daijo Shiratsuchi;Ryoji Kiyama;Takuro Kubozono;Toshihiro Takenaka;Mitsuru Ohishi . A Three-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up Study: Does Mild Cognitive Impairment Accelerate Age-Related Changes in Physical Function and Body Composition? . Cureus 2024.9Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Ryoji Kiyama, Takuro Kubozono, Toshihiro Takenaka, Mitsuru Ohishi . A Three-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up Study: Does Mild Cognitive Impairment Accelerate Age-Related Changes in Physical Function and Body Composition? . Cureus16 ( 9 ) e68605 2024.9Reviewed
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 . 高齢者におけるメタボリックシンドロームおよび身体機能低下と軽度認知障害との関連:垂水研究による横断分析 . 日本循環器予防学会誌 2024.9Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Suguru Shimokihara, Ryota Kuratsu, Yoshihiko Akasaki, Yuma Hidaka, Hyuma Makizako . Averting older adults' memory function decline via meaningful activities: A follow-up longitudinal study . European Geriatric Medicine 2024.8Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Hyuma Makizako, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Ryoji Kiyama, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi . Importance of lifestyle activities for older adults’ psychosomatic functions after driving cessation: Interpretation by a mixed-methods study . Journal of Applied Gerontology 2024.8Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Hyuma Makizako, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Ryoji Kiyama, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi . Importance of lifestyle activities for older adults’ psychosomatic functions after driving cessation: Interpretation by a mixed-methods study . Journal of Applied Gerontology 2024.8Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Suguru Shimokihara, Ryota Kuratsu, Yoshihiko Akasaki, Yuma Hidaka, Hyuma Makizako . Averting older adults' memory function decline via meaningful activities: A follow-up longitudinal study . European Geriatric Medicine 2024.8Reviewed
Tatsuya Fukuei, Shoma Akaida, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Mana Tateishi, Yukari Aishita, Ryota Kuratsu, Hyuma Makizako . Associations between driving status, frequency of transport use after driving cessation, and social frailty among middle-aged and older people aged 60 years and older . Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research28 ( 4 ) 437 - 444 2024.7Reviewed
Fukuei T, Akaida S, Taniguchi Y, Shiratsuchi D, Kiuchi Y, Tateishi M, Aishita Y, Kuratsu R, Makizako H . Associations between driving status, frequency of transport use after driving cessation, and social frailty among middle-aged and older people aged 60 years and older . Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research 2024.7Reviewed
古谷直弘, 四宮明宏, 白土大成, 土方麻衣, 坂本勇斗, 武藤健人, 牧迫飛雄馬 . 胃癌・大腸癌患者における術前のPossible Sarcopeniaと術後の合併症および在院日数との関連 ―後ろ向き観察研究― . 日本がん・リンパ浮腫理学療法学会誌 2024.6Reviewed
古谷直弘, 四宮明宏, 白土大成, 土方麻衣, 坂本勇斗, 武藤健人, 牧迫飛雄馬 . 胃癌・大腸癌患者における術前のPossible Sarcopeniaと術後の合併症および在院日数との関連 ―後ろ向き観察研究― . 日本がん・リンパ浮腫理学療法学会誌 2024.6Reviewed
Shiratsuchi D, Makizako H, Akaida S, Tateishi M, Hirano H, Iijima K, Yamada M, Kojima N, Obuchi S, Fujiwara Y, Murayama H, Nishita Y, Jeong S, Otsuka R, Abe T, Suzuki T . Associations between information and communication technology use and frailty in community-dwelling old-old adults: results from the ILSA-J. . European geriatric medicine 2024.5
Abe T, Okuyama K, Motohiro A, Shiratsuchi D, Isomura M . Combined associations of regular exercise and work-related moderate-to-vigorous physical activity with occupational stress responses: a cross-sectional study . Frontiers in Sports and Active Living 2024.5Reviewed
Shiratsuchi D, Makizako H, Akaida S, Tateishi M, Hirano H, Iijima K, Yamada M, Kojima N, Obuchi S, Fujiwara Y, Murayama H, Nishita Y, Jeong S, Otsuka R, Abe T, Suzuki T . Associations between information and communication technology use and frailty in community-dwelling old-old adults: Results from the ILSA-J. . Eur Geriatr Med 2024.5Reviewed
立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬 . フレイル高齢者に対する個別運動と集団運動による効果の相違の検証―ランダム化比較試験― . 日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Atsushi Motohiro, Kenta Okuyama, Takafumi Abe . Relationship between occupational stress and presenteeism status among workers in small and medium-sized enterprises . Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health 2024.5Reviewed
Makizako H, Akaida S, Shiratsuchi D, Tateishi M . Are middle-aged and older adult users of physical activity monitors more physically active and at a lower risk of locomotive syndrome? Cross-sectional Web-based Online Survey . Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research 2024.5Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Mana Tateishi, Ryota Kuratsu, Hyuma Makizako . Life satisfaction and awareness of meaningful activities among middle-aged adults: A population-based study . British Journal of Occupational Therapy 2024.4Reviewed
三宅悠斗, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬 . 地域在住高齢者における睡眠の質と身体機能との関連性〜共分散構造分析による介在する要因の検討〜 . 日本老年療法学会誌 2024.3Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuki Nakai, Yuto Kiuchi, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi, Hyuma Makizako . Independent Association between Cognitive Frailty and Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Community-Dwelling Older Adults . Gerontology70 ( 5 ) 1 - 8 2024.2Reviewed
Takafumi ABE, Kenta OKUYAMA, Atsushi MOTOHIRO, Daijo SHIRATSUCHI, Minoru ISOMURA . Association between different types of physical activity and occupational stress in Japanese workers: a cross-sectional study . Industrial Healthadvpub ( 0 ) 2024.1Reviewed
Norio Yamamoto, Shunsuke Taito, Takanori Miura, Takashi Ariie, Yosuke Tomita, Hirofumi Ogihara, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Takashi Yorifuji, Yasushi Tsujimoto . Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic re-views in orthopedic journals: A meta-epidemiological study . Journal of Clinical Medicine12 ( 22 ) 7031 - 7031 2023.11Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Mana Tateishi, Shoma Akaida, Chika Tagata, Makoto Kobayashi, Takanobu Takihara . Association between muscle weakness and cap-grasping patterns when opening plastic bottles in community-dwelling older adults. . Geriatrics & gerontology international23 ( 10 ) 758 - 760 2023.9Reviewed
Takahiro Tsuge, Norio Yamamoto, Shunsuke Taito, Takanori Miura, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Takashi Yorifuji . Efficacy of telerehabilitation for patients after hip fracture surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. . Journal of telemedicine and telecare31 ( 2 ) 1357633X231181632 - 183 2023.7Reviewed International journal
Kento Muto, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kazuki Nanbu, Hayato Sakamoto, Naohiro Furuya, Kazushi Nakamura, Mitani Yushi, Nako Tsujita, Hyuma Makizako . Ability to walk 10 m within the first week of stroke predicts independent outdoor walking and destination. . Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases : the official journal of National Stroke Association32 ( 8 ) 107145 - 107145 2023.5International journal
坂本 勇斗, 白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬 . 脳腫瘍患者に対するWiiの介入効果 スコーピングレビュー . 保健医療学雑誌14 ( 1 ) 45 - 52 2023.4
SHIRATSUCHI Daijo, MAKIZAKO Hyuma, AKAIDA Shoma, SHONO Saki, SHIIBA Ryuhei, TANIGUCHI Yoshiaki, TOMIOKA Kazutoshi, SATO Nana, WADA Ayumi, KIUCHI Yuto, TATEISHI Mana, NAKAI Yuki . Association of Changes in Low Back Pain in Workers and Presenteeism Following an Epidemic of Novel Coronavirus Infection . Physical Therapy Japan49 ( 5 ) 339 - 347 2022.10
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Yuki Nakai, Seongryu Bae, Sangyoon Lee, Hunkyung Kim, Yuriko Matsuzaki-Kihara, Ichiro Miyano, Hidetaka Ota, Hiroyuki Shimada . Associations of fall history and fear of falling with multidimensional cognitive function in independent community-dwelling older adults: findings from ORANGE study. . Aging clinical and experimental research34 ( 12 ) 2985 - 2992 2022.9International journal
Yuki Nakai, Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Tomomi Akanuma, Kaori Yokoyama . Association of Sleep Quality Status With Worsening Low Back or Knee Pain During The COVID-19 State of Emergency Among Old-Old Adults. . Pain management nursing : official journal of the American Society of Pain Management Nurses23 ( 4 ) 473 - 477 2022.8International journal
Shoma Akaida, Yuki Nakai, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kazutoshi Tomioka, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Nana Sato, Ayumi Wada, Yuto Kiuchi, Saki Shono, Ryuhei Shiiba, Mana Tateishi, Hyuma Makizako . Association of self-rated health with type and frequency of social interaction during the declaration of COVID-19 state of emergency among Japanese community-dwelling oldest-old adults. . Geriatrics & gerontology international22 ( 5 ) 405 - 411 2022.5
MAIZAKO Hyuma, SHIRATSUCHI Daijo, SHIIBA Ryuhei, TANIGUCHI Yoshiaki, KUBOZONO Takuro, OHISHI Mitsuru . Correlation of sarcopenia with orthopedic disorders, history of falls, and polypharmacy among community-dwelling older adults . Journal of Physical Therapy for Prevention1 ( 0 ) 19 - 24 2022.3Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Saki Shono, Ryuhei Shiiba, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Kazutoshi Tomioka, Nana Sato, Ayumi Wada, Yuto Kiuchi, Mana Tateishi, Yuki Nakai . Associations Between Health Literacy and Changes in Exercise Behavior During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 State of Emergency Among Middle-Aged Adults: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey. . Asia-Pacific journal of public health34 ( 2-3 ) 286 - 289 2022.3International journal
福原 みなみ, 橋本 幸成, 白土 大成, 高野 文音 . 他人の手徴候の改善に運動麻痺の軽減が関与したと考えられた1症例 . 高次脳機能研究41 ( 4 ) 413 - 420 2021.12
Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Saki Shono, Ryuhei Shiiba, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yuki Nakai . Physical Activity and Perceived Physical Fitness during the COVID-19 Epidemic: A Population of 40- to 69-Year-Olds in Japan. . International journal of environmental research and public health18 ( 9 ) 2021.5International journal
Hyuma Makizako, Yuki Nakai, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Tomomi Akanuma, Kaori Yokoyama, Yuriko Matsuzaki-Kihara, Hiroto Yoshida . Perceived declining physical and cognitive fitness during the COVID-19 state of emergency among community-dwelling Japanese old-old adults. . Geriatrics & gerontology international21 ( 4 ) 364 - 369 2021.4
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Yuki Nakai, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Tomomi Akanuma, Kaori Yokoyama, Yuriko Matsuzaki-Kihara, Hiroto Yoshida . Association of Health Literacy with the Implementation of Exercise during the Declaration of COVID-19 State of Emergency among Japanese Community-Dwelling Old-Old Adults. . International journal of environmental research and public health18 ( 4 ) 1 - 9 2021.2International journal
白土 大成, 橋本 幸成, 濱田 則雄, 永利 聡仁, 吉田 大輔 . 急性期病院における脳梗塞発症時の 大腰筋面積が転帰に及ぼす影響—─腹部CTを用いた後ろ向きコホート研究─ . 理学療法科学35 ( 2 ) 257 - 261 2020Reviewed
元廣惇, 藤井寛幸, 編 白土大成, 由利拓真, 爲國友梨香( Role: Joint author , Part 3 Chapter2 働く人の「生産性」と「エンゲージメント)
株式会社 クリエイツかもがわ 2023.11 ( ISBN:9784863423619 )
リハビリテーション医学
上月正博, 高橋仁美・編, 牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成( Role: Contributor , 6 サルコペニア,フレイル対策)
メジカルビュー社 2021.9 ( ISBN:9784758320610 )
地域在住高齢者における慢性疼痛がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響:睡眠の媒介効果 Reviewed
白土大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 桑波田 聡, 大石 充
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
Close-up 遠隔理学療法 フレイル・サルコペニアに対する遠隔理学療法の現状 Reviewed
白土大成
理学療法ジャーナル 59 ( 12 ) 1462 - 1465 2025.12
地域在住⾼齢者における夜間排尿の頻度と転倒歴との関連 Reviewed
伊香 孝則, 白土 大成, 田平 健人, 三宅 悠斗, 愛下 由香里, 倉津 諒大, 與 祥子, 洋樹, 福森 愛美, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第4回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2025.12
地域在住高齢者における聴覚機能低下と骨格筋健康指標の関連:軽度認知障害を媒介とした縦断的分析 Reviewed
白土大成, 三宅悠斗, 田平健人, 倉津諒大, 木山良二, 川田将之, 牧迫飛雄馬
第4回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2025.12
地域在住高齢者におけるフレイルの悪化と改善の要因 —基本チェックリスト評価による5年間の変化― Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 三宅悠斗, 田平健人, 田平隆行, 木山良二, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充
第4回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2025.12
地域在住女性高齢者におけるサルコペニアと下部尿路症状および尿失禁不安との関連 Reviewed
愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 木内悠人, 立石麻奈, 木山良二
第11回日本ウィメンズヘルス・メンズヘルス理学療法学会学術大会 2025.12
地域在住中高齢者における立ち上がり動作時の床反力指標の性別による加齢変化パターンの違い Reviewed
三宅悠斗, 白土大成, 田平健人, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第4回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2025.12
地域在住中高齢者におけるメタボリックシンドロームが体組成および身体機能の3年間の変化に及ぼす影響 Reviewed
西洋樹, 牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 木内悠人, 三宅悠斗, 田平健人, 與祥子, 福森愛美, 倉津諒大, 愛下由香里, 川田将之, 木山良二, 竹中俊宏, 窪園琢郎, 大石充
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
通いの場に参加する地域在住高齢者のおすそわけ形式と抑うつの関連 Reviewed
與 祥子, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 木内 悠人, 三宅 悠斗, 西 洋樹, 福森 愛美, 田平 健人, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
多様な生活活動の実践は高齢者の身体機能維持に有用か?横断解析および5年間の縦断解析 Reviewed
白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 三宅 悠斗, 田平 健人, 倉津 諒大, 西 洋樹, 與 祥子, 福森 愛美, 伊香 孝則, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
地域在住高齢者における筋量および筋質の組み合わせと身体機能低下との関連 Reviewed
三宅 悠斗, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 田平 健人, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
地域在住高齢者におけるフレイルとスマートフォン使用状況との関連 Reviewed
福森愛美, 白土大成, 田平 健人, 赤井田将真, 木内悠人, 三宅 悠斗, 西 洋樹, 與 祥子, 田平 隆行, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
地域在住高齢者におけるスマートフォン習熟度と下肢機能との関連とその性差 Reviewed
田平健人, 三宅悠斗, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 田平隆行, 下木原俊, 牧迫飛雄馬
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
高齢脳梗塞患者における自宅退院時身体機能と6ヶ月後生活空間との関連:抑うつの媒介効果 Reviewed
武藤 健人, 白土 大成, 松元 大修, 永井将貴, 久保田雅史
第12回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2025.11
An index to assess frailty status and intrinsic capacity among older Japanese adults requiring long-term care Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kento Tabira, Yuto Miyake, Yukiko Nishita, Mana Tateishi, Mai Kabayama, Kei Kamide, Yukiko Nishita, Rei Otsuka
11th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2025.10
Validation of the frailty–intrinsic capacity index among older Japanese adults using day services or who were admitted to geriatric health service facilities Reviewed
Kento Tabira, Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yuto Miyake, Yukiko Nishita, Mana Tateishi, Mai Kabayama, Kei Kamide, Rei Otsuka
11th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2025.10
Longitudinal Association between Low Muscle Mass and Changes in Ground Reaction Force Parameters during Sit-to-Stand Motion among Community-Dwelling Older Adults Reviewed
Yuto Miyake, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kento Tabira, Ryoji Kiyama, Hyuma Makizako
11th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2025.10
Association between intrinsic capacity and self-rated health: a 3-year longitudinal study Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yuto Miyake, Kento Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Rei Otsuka, Hyuma Makizako
11th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2025.10
内在的能力は身体的フレイルの悪化および改善に寄与するか?―5年間の前向き研究― Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 三宅悠斗, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 大塚礼, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 大石充
第67回日本老年医学会学術集会 2025.6
地域在住高齢者におけるボランティア・エンゲイジメントと認知機能の関連 Reviewed
白土大成, 三宅悠斗, 倉津諒大, 西洋樹, 福森愛美, 與祥子, 木山良二, 小坂元理恵子, 田中博美, 牧迫飛雄馬
第67回日本老年医学会学術集会 2025.6
Associations Between Lifestyle Habits and Worl-Related Stress in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Workers: A Comparison of Blue and White Collar Workers Reviewed
Yurika Tamekuni, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Takuma Yuri, Kousuke Wakushima, Atsushi Motohiro
The 8th Asia Pacific Occupational Therapy Congress 2024 (APOTC 2024) 2024.11
高齢者のフレイルと生活満足度の関連における社会との関わりの媒介効果 Reviewed
赤井田将真, 白土大成, 三宅悠人, 福榮竜也, 牧迫飛雄馬
第11回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2024.11
地域在住高齢者における昼寝習慣と身体機能および筋量との関連 Reviewed
三宅 悠斗, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木山 良二, 川田 将之, 桑波田 聡, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第11回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2024.11
地域在住高齢者におけるフレイルおよび内在的能力と主観的健康感の関連 Reviewed
白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 三宅 悠斗, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 大塚 礼, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第11回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2024.11
Is life satisfaction associated with awareness of meaningful activities among middle-aged adults? Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Mana Tateishi, Ryota Kuratsu, Hyuma Makizako
The 8th Asia Pacific Occupational Therapy Congress 2024 (APOTC 2024) 2024.11
Association of frailty and intrinsic capacity with subjective health in community-dwelling older adults Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Yuto Miyake, Ryoji Kiyama, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Rei Otsuka, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
Effect of ground reaction force in sit-to-stand motion on deteriorated frailty among community- dwelling older adults Reviewed
Yuto Miyake, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Mana Tateishi, Ryotra Kuratsu, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
Intrinsic capacity as protect and remission factors for frailty: Results from 3-years prospective cohort study Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Shoma Akaida, Yuto Miyake, Ryoji Kiyama, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Rei Otsuka, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
Association of frailty and intrinsic capacity with subjective health in community-dwelling older adults Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Yuto Miyake, Ryoji Kiyama, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Rei Otsuka, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
Intrinsic capacity as protect and remission factors for frailty: Results from 3-years prospective cohort study Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Shoma Akaida, Yuto Miyake, Ryoji Kiyama, Takayuki Tabira, Mana Tateishi, Rei Otsuka, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
Effect of ground reaction force in sit-to-stand motion on deteriorated frailty among community- dwelling older adults Reviewed
Yuto Miyake, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Mana Tateishi, Ryotra Kuratsu, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
10th Asian Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia 2024.10
介護福祉事業所の健康経営に対する鹿児島大学オンラインヘルスラボ(KU-OHL)の活用可能性 Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 田平隆行, 白浜幸高, KU-OHL project team
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
地域在住高齢者における身だしなみと外出頻度および認知機能の関連 Reviewed
赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 三宅悠斗, 牧迫飛雄馬
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
地域在住高齢者における慢性疼痛がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響:睡眠の媒介効果 Reviewed
白土大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 桑波田 聡, 大石 充
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
地域在住高齢者における安静時エネルギー消費量の推算式によるサルコペニアの推測可能性の検討 Reviewed
三宅悠斗, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
地域在住後期高齢者における長時間睡眠と歩行速度との関連 Reviewed
立石麻奈, 牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 桑波田聡, 大石充
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.8
介護福祉事業所の健康経営に対する鹿児島大学オンラインヘルスラボ(KU-OHL)の活用可能性 Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 田平隆行, 白浜幸高, KU-OHL project team
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における安静時エネルギー消費量の推算式によるサルコペニアの推測可能性の検討 Reviewed
三宅悠斗, 白土大成, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における身だしなみと外出頻度および認知機能の関連 Reviewed
赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 三宅悠斗, 牧迫飛雄馬
第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における運動習慣および栄養状態と筋量、運動機能との関連 Reviewed
立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
起立動作測定における床反力計測の有用性についての検討 ~性別ごとの加齢変化における評価方法の比較~ Reviewed
倉津 諒大, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における意味のある活動の満足度および遂行度が3年後の認知機能に及ぼす影響 Reviewed
赤井田将真, 田平隆行, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 下木原俊, 倉津諒大, 赤﨑義彦, 日高雄磨, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
中高齢者におけるα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型と身体機能および身体組成の関連性に対する運動・食習慣の影響. Reviewed
白土大成, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 谷口善昭, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
コロナ禍で高齢女性の筋力および骨格筋量の加齢変化は加速したのか? Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 大石充
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
コロナ禍で高齢女性の筋力および骨格筋量の加齢変化は加速したのか? Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 大石充
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
起立動作測定における床反力計測の有用性についての検討 ~性別ごとの加齢変化における評価方法の比較~. Reviewed
倉津 諒大, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における運動習慣および栄養状態と筋量、運動機能との関連. Reviewed
立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
地域在住高齢者における意味のある活動の満足度および遂行度が3年後の認知機能に及ぼす影響. Reviewed
赤井田将真, 田平隆行, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 下木原俊, 倉津諒大, 赤﨑義彦, 日高雄磨, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
中高齢者におけるα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型と身体機能および身体組成の関連性に対する運動・食習慣の影響. Reviewed
白土大成, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 谷口善昭, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第66回日本老年医学会 2024.6
高齢者の飲酒習慣が与える睡眠との関連 Reviewed
西尾育子, 山下亜矢子, 牧迫飛雄馬, 田平隆行, 池田由里子, 益満智美, 大重匡, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, KU-OHLプロジェクトチーム
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
中高齢者における意味のある活動の実施状況と抑うつの関係:自動車運転状況による層別解析 Reviewed
赤井田将真, 福榮竜也, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
60歳以上の地域在住中高齢者における動脈硬化が筋量、握力、歩行速度に与える影響 ―4年間の縦断研究― Reviewed
谷口善昭, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大, 愛下由香里, 大石充
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
地域在住高齢者におけるA Body Shape Indexと肥満および低筋量の併存との関連性 Reviewed
三宅 悠斗, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
地域在住高齢者における睡眠時間および睡眠の質がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響 Reviewed
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 桑波田 聡, 大石 充
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
地域在住高齢者における身体活動および食品多様性と軽度認知障害との関連 Reviewed
木内悠人, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 倉津諒大, 木村美佳, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 大石充
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
地域在住高齢者の起立動作のパワー/スピード/バランス能力と認知機能低下との関連 Reviewed
倉津 諒大, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
運動習慣を有するフレイルおよびプレフレイル高齢者における緑茶の摂取頻度と身体機能・身体組成との関連 Reviewed
立石麻奈, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 倉津諒大, 白土大成, 瀧原孝宣, 田形千佳, 小林誠, 馬場吉武
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
労働者における身体活動と職業性ストレスの関係
安部孝文, 奥山健太, 元廣惇, 白土大成
第62回山陰体育学会 2024.1
中小企業勤労者におけるワーク・エンゲイジメントと慢性疾患、ストレス、心理的安全性の関連性についての検討
爲國友梨香, 元廣惇, 白土大成, 由利拓真
第57回日本作業療法学会 2023.11
地域在住高齢女性の自動車運転状況と認知機能との関連 Reviewed
赤井田 将真, 白土大成, 木内悠人, 立石麻奈, 牧迫飛雄馬
第57回日本作業療法学会 2023.11
股関節近位部骨折手術後の患者に対するTelerehabilitationの有効性:システマティック・レビューとメタアナリシス
柘植 孝浩, 山本 乃利男, 對東 俊介, 三浦 隆徳, 白土 大成, 頼藤 貴志
2023.11
Associations of Engagement in Various Lifestyle Activities with Physical Function and Muscle Mass Among Community-dwelling Middle-aged and Older Adults after Cessation of Driving: A Mixed-methods Study Reviewed
Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Yuki Nakai, Ryoji Kiyama, Hyuma Makizako
9th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2023.10
Associations between information and communication technology use and physical frailty in community-dwelling old-old adults: findings from ILSA-J Reviewed
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Yukiko Nishita, Seungwon Jeong, Rei Otsuka, Takumi Abe, Takao Suzuki
9th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2023.10
Achieving recommended levels of moderate physical activity: Alleviating age-related weakness but not loss of muscle mass Reviewed
Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Mana Tateishi, Tatsuya Fukuei
9th Asian Conference for Frailty and Sarcopenia 2023.10
60歳以上の中高齢者における勇気ある思考や行動と主観的健康感との関連性 Reviewed
谷口善昭, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 牧迫飛雄馬
第10回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2023.10
地域在住中高年者におけるCOVID-19流行禍の身体活動量の自己管理が3年後の身体機能に与える影響 Reviewed
立石 麻奈, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 竹中 俊宏, 前田真由佳, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2023.9
主観的な睡眠の質と身体機能との関連性〜共分散構造分析による検討〜 Reviewed
三宅 悠斗, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2023.9
地域在住中高齢者における靴底の状態と転倒との関連性 Reviewed
白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 福榮 竜也, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2023.9
地域在住高齢者における新聞を読む頻度と認知機能の関連 Reviewed
倉津 諒大, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 木内悠人, 愛下 由香里, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2023.9
地域在住高齢者における身体機能と認知機能との関連について~教育歴による差異~
倉津 諒大, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 大石 充, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第12回日本認知症予防学会学術集会 2023.9
高齢者が自動車運転中止後に様々な活動に取り組むために重要な要素についての検討:計量テキスト分析 Reviewed
赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 2023.9
Does mild cognitive impairment accelerate age-related changes in physical function and body composition? -A 3-years longitudinal follow-up study-
Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Ryoji Kiyama, Masayuki Kawada, Takayuki Tabira, Hiroyuki Shimada, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi
IAGG Asia/Oceania 2023 2023.6
地域在住高齢者における外出頻度および社会的交流と動脈硬化の関連
赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充, 牧迫飛雄馬
第59回日本循環器予防学会学術集会 2023.6
地域在住高齢者におけるメタボリックシンドロームおよび身体機能低下の併存と認知機能の関連
白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 谷口善昭, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充
2023.6
地域在住高齢者におけるペットボトル開封時のキャップ把持パターンと筋力低下の関連性 Reviewed
白土大成, 谷口善昭, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 愛下由香里, 福榮竜也, 倉津諒大, 牧迫飛雄馬
第65回日本老年医学会学術集会 2023.6
地域在住高齢者におけるMotoric cognitive risk syndromeと転倒恐怖感との関連
倉津諒大, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 福榮竜也, 愛下由香里, 牧迫飛雄馬
2023.6
地域在住中高齢者の自動車運転実施状況および生活活動と身体機能、筋量との関連
赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 谷口善昭, 白土大成, 木内悠人, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充, 牧迫飛雄馬
2023.6
アクチニン遺伝子多型が身体機能の加齢変化に及ぼす影響―3年間の縦断観察研究—
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充
2023.6
中小企業勤労者における職業性ストレスとプレゼンティーズムとの関連
白土 大成, 元廣 惇, 奥山 健太, 安部 孝文
産業衛生学雑誌 65 ( 臨増 ) 326 - 326 2023.5
看護師におけるワーク・エンゲイジメントと腰痛、ストレスおよび自己効力感の関連性
愛下 由香里, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 宇都 良大, 福榮 竜也, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 田中 梨美子, 柳 正和, 連 利博
産業衛生学雑誌 65 ( 臨増 ) 514 - 514 2023.5
【COVID-19とフレイルの実際】COVID-19とフレイルの実際 フレイルの社会的側面
白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬
日本老年医学会雑誌 60 ( 2 ) 127 - 134 2023.4
自動車運転をしていない地域在住後期高齢女性における免許保有歴と認知機能の関連
赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 福榮 竜也, 白土 大成, 愛下 由香里, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第33回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2023.3
Shiratsuchi D., Makizako H., Tateishi M., Akaida S., Tagata C., Kobayashi M., Takihara T.
Geriatrics and Gerontology International 23 ( 10 ) 758 - 760 2023
地域在住高齢者における社会的交流および外出頻度と動脈硬化の関連
赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本循環器病予防学会誌 58 ( 2 ) 2023
地域在住高齢者における座位の中断回数および連続座位パターンとサルコペニアの関連性 Reviewed
福榮 竜也, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 谷口 善昭, 赤井田将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 愛下 由香里, 富岡 一俊, 中井 雄貴
第9回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2022.11
中年者におけるコロナ禍での外出自粛で自覚された身体の衰えが腰痛発生へ与える影響 Reviewed
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 谷口善昭, 愛下由香里, 福榮竜也, 木内悠人, 倉津諒大
第9回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2022.11
血液内科病棟における抑うつ症状に対する創作活動の効果
久保田裕, 白土大成, 立場文音, 立石実咲, 笠原由紀, 江藤健一郎
The 7th Annual Meeting of Japan Community Health care Society in KUMAMOTO 2022.10
地域包括ケア病棟入院患者における再入院に影響を及ぼす疾患の検討
The 7th Annual Meeting of Japan Community Health care Society in KUMAMOTO 2022.10
中高齢者における人生での後悔の有無と主観的幸福感との関連
第1回日本老年療法学会 2022.10
フレイルの認知度とフレイル該当の有無との関連
第1回日本老年療法学会 2022.10
コロナ禍における歩数計の利用とフレイル―60歳以上の中高齢者を対象としたWEB調査—
第9回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 6 ( Supplement ) 2022.10
The association between perceived neighborhood environment and frailty among Japanese adults aged 60 years and older
Hyuma Makizako, Tatsuya Fukuei, Shoma Akaida, Mana Tateishi, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Yuto Kiuchi, Yukari Aishita, Ryota Kuratsu
The 8th ASIAN CONFERENCE for FRAILTY AND SARCOPENIA 2022.10
Is there an association between cardio-ankle vascular index and physical and cognitive performance?
Shoma Akaida, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Yuki Nakai, Yuto Kiuchi, Mana Tateishi, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Toshihiro Takenaka, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi, Hyuma Makizako
The 8th ASIAN CONFERENCE for FRAILTY AND SARCOPENIA 2022.10
地域在住高齢者におけるPGC-1α遺伝子多型と転倒との関連
第1回日本老年療法学会 2022.10
地域在住高齢者における認知的フレイルと動脈硬化度の関連
第9回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 6 ( Supplement ) 2022.10
急性期脳卒中患者における発症1週間後の10m歩行の可否は退院時屋外自立歩行と退院先に関連する
第20回日本神経理学療法学会学術大会 2022.10
自動車運転を中止した中高年者における交通の利用頻度と社会的フレイルの関連性
第9回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 6 ( Supplement ) 2022.10
COVID-19流行禍における中年期の運動自己効力感に関連する要因
立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬
2022.9
60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 谷口善昭, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 白土大成
日本転倒予防学会誌(Web) 9 ( 2 ) 2022
歩数計の利用と身体活動量およびロコモティブシンドロームとの関連
牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 生野佐紀
日本老年医学会雑誌 59 2022
中高齢者の人生における最大の後悔が生じる生活領域と性差に関する研究
赤井田将真, 生野佐紀, 立石麻奈, 谷口善昭, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本老年医学会雑誌 59 2022
フレイル高齢者に対する個別運動と集団運動の介入効果の違い-ランダム化比較試験-
立石麻奈, 赤井田将真, 生野佐紀, 椎葉竜平, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本老年医学会雑誌 59 2022
COVID-19の流行に伴う緊急事態宣言中の生活習慣の変化と主観的幸福感との関係
生野佐紀, 赤井田将真, 赤井田将真, 椎葉竜平, 椎葉竜平, 白土大成, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 木内悠人, 立石麻奈, 立石麻奈, 中井雄貴, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本疫学会学術総会講演集(Web) 32nd 2022
地域在住高齢者におけるα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型と筋量および身体機能との関連
白土大成, 谷口善昭, 木内悠人, 赤井田将真, 窪薗琢郎, 大石充, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本老年医学会雑誌 59 2022
Association of Changes in Low Back Pain in Workers and Presenteeism Following an Epidemic of Novel Coronavirus Infection
白土大成, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 赤井田将真, 生野佐紀, 椎葉竜平, 椎葉竜平, 谷口善昭, 谷口善昭, 富岡一俊, 佐藤菜々, 和田あゆみ, 木内悠人, 木内悠人, 立石麻奈, 立石麻奈, 中井雄貴
理学療法学(Web) 49 ( 5 ) 2022
【疾患別にみたサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際】運動器疾患患者のサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際
白土 大成, 椎葉 竜平, 牧迫 飛雄馬
理学療法 38 ( 11 ) 988 - 995 2021.11
地域在住高齢者における前糖尿病および糖尿病と筋量、筋力、身体機能との関係
第8回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2021.11
ウィズコロナにおける勤労者の腰痛の変化とプレゼンティーズムとの関連
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 生野 佐紀, 椎葉 竜平, 谷口 善昭, 富岡 一俊, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 中井 雄貴
第4回日本産業理学療法研究会学術大会 2021.11
Associations between health literacy and exercise behavior changes during the COVID-19 state of emergency among middle-aged Japanese adults
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Hyuma Makizako, Shoma Akaida, Saki Shono, Ryuhei Shiiba, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Kazutoshi Tomioka, Nana Sato, Ayumi Wada, Yuto Kiuchi, Mana Tateishi, Yuki Nakai
International Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 2021 2021.6
COVID-19流行下における脳の衰えの自覚と勤務形態および運動機会・運動量の変化との関係
第10回日本認知症予防学会学術集会 2021.6
Association between presenteeism and low back pain among nurses in a Japanese acute care hospital: a cross-sectional study
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kosei Hashimoto, Norio Hamada, Setaka Kasumi, Daisuke Yoshida
World Physiotherapy Congress2021 2021.4
地域在住高齢者における新型コロナウイルス感染症(COVID-19)流行による日常生活の変化とフレイルおよびうつ傾向との関連
第3回日本体力医学会南九州地方会 2021.2
疾患別にみたサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際 運動器疾患患者のサルコペニアに対する理学療法の考え方と実際
白土大成, 椎葉竜平, 牧迫飛雄馬
理学療法(東京) 38 ( 11 ) 2021
地域在住中高年者におけるメタボリックシンドロームと食品摂取多様性との関連
白土大成, 白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 赤井田将真, 木内悠人, 木内悠人, 谷口善昭, 谷口善昭, 椎葉竜平, 椎葉竜平, 生野佐紀, 生野佐紀, 福榮竜也, 福榮竜也, 叶内宏明, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢朗, 大石充
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会誌 5 ( Supplement ) 2021
The factors related to the manifestation of posterior-variant Alien hand syndrome
福原みなみ, 橋本幸成, 白土大成, 高野文音
日本作業療法学会抄録集(CD-ROM) 55th 2021
地域在住中高齢者における骨量・筋量低下とα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型との関連性
谷口善昭, 谷口善昭, 牧迫飛雄馬, 中井雄貴, 富岡一俊, 佐藤菜々, 和田あゆみ, 木内悠人, 木内悠人, 赤井田将真, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 立石麻奈, 生野佐紀, 生野佐紀, 椎葉竜平, 椎葉竜平, 白土大成, 白土大成
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会誌 5 ( Supplement ) 2021
地域在住後期高齢者におけるCOVID-19に伴う緊急事態宣言中の社会的交流と主観的健康感との関係
赤井田将真, 中井雄貴, 谷口善昭, 佐藤菜々, 木内悠人, 椎葉竜平, 生野佐紀, 白土大成, 立石麻奈, 牧迫飛雄馬
日本老年医学会雑誌 58 2021
地域在住後期高齢者におけるペットボトル開閉の困難感とフレイルとの関連性
谷口善昭, 牧迫飛雄馬, 中井雄貴, 白土大成, 赤沼智美, 横山香理, 松崎由里子, 吉田裕人
日本老年医学会雑誌 58 2021
地域在住高齢者におけるヘルスリテラシーとCOVID-19緊急事態宣言中の運動実施との関連
白土大成, 牧迫飛雄馬, 中井雄貴, 谷口善昭, 赤沼智美, 横山香理, 松崎由里子, 吉田裕人
日本老年医学会雑誌 58 2021
後期高齢者におけるCOVID-19による緊急事態宣言後の体力および脳の衰えの自覚
牧迫飛雄馬, 中井雄貴, 白土大成, 赤沼智美, 横山香理, 松崎由里子, 吉田裕人
日本老年医学会雑誌 58 2021
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 (一社)日本転倒予防学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 (一社)日本転倒予防学会
西尾 育子, 山下 亜矢子, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 田平 隆行, 池田 由里子, 益満 智美, 大重 匡, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, KU-OHLプロジェクトチーム 高齢者の睡眠と生活習慣との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 倉津 諒大, 白土 大成, 瀧原 孝宣, 田形 千佳, 小林 誠, 馬場 吉武 運動習慣を有するフレイルおよびプレフレイル高齢者における緑茶の摂取頻度と身体機能・身体組成との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
倉津 諒大, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者の起立動作のパワー/スピード/バランス能力と認知機能低下との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
木内 悠人, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 倉津 諒大, 木村 美佳, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 大石 充 地域在住高齢者における身体活動および食品多様性と軽度認知障害との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 桑波田 聡, 大石 充 地域在住高齢者における睡眠時間および睡眠の質がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
三宅 悠斗, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるA Body Shape Indexと肥満および低筋量の併存との関連性
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
赤井田 将真, 福榮 竜也, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬 中高齢者における意味のある活動の実施状況と抑うつの関係 自動車運転状況による層別解析
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
谷口 善昭, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 愛下 由香里, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 60歳以上の地域在住中高齢者における動脈硬化が握力,歩行速度,筋量に与える影響 4年間の縦断研究
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 (一社)日本転倒予防学会
赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 三宅 悠人, 福榮 竜也, 牧迫 飛雄馬 高齢者のフレイルと生活満足度の関連における社会との関わりの媒介効果
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
倉津 諒大, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 牧迫 飛雄馬 起立動作測定における床反力計測の有用性についての検討 性別ごとの加齢変化における評価方法の比較
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
立石 麻奈, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 愛下 由香里, 大石 充, 油田 幸子, 今村 佳代子, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者における運動習慣および栄養状態と筋量,身体機能との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
三宅 悠斗, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木山 良二, 川田 将之, 桑波田 聡, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者における昼寝習慣と身体機能および筋量との関連
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
赤井田 将真, 田平 隆行, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 下木原 俊, 倉津 諒大, 赤崎 義彦, 日高 雄磨, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者における意味のある活動の満足度および遂行度が3年後の認知機能に及ぼす影響
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 三宅 悠斗, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 大塚 礼, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるフレイルおよび内在的能力と主観的健康感の関連
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2024.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬 中高齢者におけるα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型と身体機能および身体組成の関連性に対する運動・食習慣の影響
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 大石 充 コロナ禍で高齢女性の筋力および骨格筋量の加齢変化は加速したのか?
日本老年医学会雑誌 2024.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 (一社)日本転倒予防学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 (一社)日本転倒予防学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 白土 大成, 三宅 悠斗, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 大塚 礼, 大石 充 内在的能力は身体的フレイルの悪化および改善要因となり得るか? 5年間の前向き研究
日本老年医学会雑誌 2025.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土 大成, 三宅 悠斗, 倉津 諒大, 西 洋樹, 福森 愛美, 與 祥子, 木山 良二, 小坂元 理恵子, 田中 博美, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるボランティア・エンゲイジメントと認知機能の関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2025.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
Daijo Shiratsuchi 一般企業の健康づくりに作業療法の観点を生かす 企業での健康づくりに関する研究
Rehatech Links株式会社 2023.9
Yvonne van Zaanen, Veena Raigangar, Daijo Shiratsuchi IFPOHE working together meeting Invited
World Physiotherapy Congress 2023 2023.6
福榮 竜也, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 倉津 諒大 自動車運転を中止した中高年者における交通の利用頻度と社会的フレイルの関連性
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2022.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 生野 佐紀 歩数計の利用と身体活動量およびロコモティブシンドロームとの関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2022.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 中井 雄貴, 白土 大成, 赤沼 智美, 横山 香理, 松崎 由里子, 吉田 裕人 後期高齢者におけるCOVID-19による緊急事態宣言後の体力および脳の衰えの自覚
日本老年医学会雑誌 2021.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
福原 みなみ, 橋本 幸成, 白土 大成, 高野 文音 後方病変型他人の手徴候を呈した1症例 症状出現に関与した要因の検討
日本作業療法学会抄録集 2021.9 (一社)日本作業療法士協会
赤井田 将真, 谷口 善昭, 中井 雄貴, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者における認知的フレイルと動脈硬化度の関連
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2022.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 中井 雄貴, 谷口 善昭, 赤沼 智美, 横山 香理, 松崎 由里子, 吉田 裕人 地域在住高齢者におけるヘルスリテラシーとCOVID-19緊急事態宣言中の運動実施との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2021.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 赤井田 将真, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型と筋量および身体機能との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2022.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
谷口 善昭, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 中井 雄貴, 白土 大成, 赤沼 智美, 横山 香理, 松崎 由里子, 吉田 裕人 地域在住後期高齢者におけるペットボトル開閉の困難感とフレイルとの関連性
日本老年医学会雑誌 2021.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
赤井田 将真, 中井 雄貴, 谷口 善昭, 佐藤 菜々, 木内 悠人, 椎葉 竜平, 生野 佐紀, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住後期高齢者におけるCOVID-19に伴う緊急事態宣言中の社会的交流と主観的健康感との関係
日本老年医学会雑誌 2021.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
谷口 善昭, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 中井 雄貴, 富岡 一俊, 佐藤 菜々, 和田 あゆみ, 木内 悠人, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 生野 佐紀, 椎葉 竜平, 白土 大成 地域在住中高齢者における骨量・筋量低下とα-アクチニン3遺伝子多型との関連性
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2021.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 木内 悠人, 谷口 善昭, 椎葉 竜平, 生野 佐紀, 福榮 竜也, 叶内 宏明, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢朗, 大石 充 地域在住中高年者におけるメタボリックシンドロームと食品摂取多様性との関連
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2021.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
赤井田 将真, 生野 佐紀, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬 中高齢者の人生における最大の後悔が生じる生活領域と性差に関する研究
日本老年医学会雑誌 2022.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
立石 麻奈, 赤井田 将真, 生野 佐紀, 椎葉 竜平, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬 フレイル高齢者に対する個別運動と集団運動の介入効果の違い ランダム化比較試験
日本老年医学会雑誌 2022.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 福榮 竜也, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 倉津 諒大 コロナ禍における歩数計の利用とフレイル 60歳以上の中高齢者を対象としたWEB調査
日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会雑誌 2022.10 (一社)日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会
生野 佐紀, 赤井田 将真, 椎葉 竜平, 白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 中井 雄貴, 牧迫 飛雄馬 COVID-19の流行に伴う緊急事態宣言中の生活習慣の変化と主観的幸福感との関係
Journal of Epidemiology 2022.1 (一社)日本疫学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成 60歳以上の中高齢者におけるフレイルと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本転倒予防学会誌 2022.9 日本転倒予防学会
赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者における社会的交流および外出頻度と動脈硬化の関連
日本循環器病予防学会誌 2023.5 (一社)日本循環器病予防学会
白土 大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 地域在住高齢者におけるメタボリックシンドロームおよび身体機能低下の併存と認知機能の関連
日本循環器病予防学会誌 2023.5 (一社)日本循環器病予防学会
白土 大成, 元廣 惇, 奥山 健太, 安部 孝文 中小企業勤労者における職業性ストレスとプレゼンティーズムとの関連
産業衛生学雑誌 2023.4 (公社)日本産業衛生学会
愛下 由香里, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 宇都 良大, 福榮 竜也, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 田中 梨美子, 柳 正和, 連 利博 看護師におけるワーク・エンゲイジメントと腰痛、ストレスおよび自己効力感の関連性
産業衛生学雑誌 2023.4 (公社)日本産業衛生学会
牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 竹中 俊宏, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充 α-アクチニン3遺伝子多型が身体機能の加齢変化に及ぼす影響 3年間の縦断観察研究
日本老年医学会雑誌 2023.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住中高齢者の自動車運転実施状況および生活活動と身体機能,筋量との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2023.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
倉津 諒大, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 立石 麻奈, 福榮 竜也, 愛下 由香里, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるMotoric cognitive risk syndromeと転倒恐怖感との関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2023.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 愛下 由香里, 福榮 竜也, 倉津 諒大, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢者におけるペットボトル開栓時のキャップ把持パターンと筋力低下の関連性
日本老年医学会雑誌 2023.5 (一社)日本老年医学会
白土大成 包括的観察研究による生活機能低下の気付きの支援
第34回日本老年医学会九州地方会 2024.3
白土大成 サルコペニア・フレイルに対する予防理学療法の実践―参加を見据えた理学療法―
第10回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 2023.10
Tateishi Mana, Akaida Shoma, Taniguchi Yoshiaki, Kiuchi Yuto, Shiratsuchi Daijo, Makizako Hyuma COVID-19パンデミック下での中年成人における運動自己効力感と関連する因子(Factors associated with exercise self-efficacy among middle-aged adults during the COVID-19 pandemic)
The Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine 2022.11 (一社)日本体力医学会
赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 福榮 竜也, 白土 大成, 愛下 由香里, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬 自動車運転をしていない地域在住後期高齢女性における免許保有歴と認知機能の関連
日本老年医学会雑誌 2023.10 (一社)日本老年医学会
赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬 地域在住高齢女性における自動車運転の経験と認知機能の関連
日本作業療法学会抄録集 2023.11 (一社)日本作業療法士協会
爲國 友梨香, 元廣 惇, 白土 大成, 由利 拓真 中小企業労働者におけるワーク・エンゲイジメントと慢性疾患,ストレス,心理的安全性の関連性についての検討
日本作業療法学会抄録集 2023.11 (一社)日本作業療法士協会
柘植 孝浩, 山本 乃利男, 對東 俊介, 三浦 隆徳, 白土 大成, 頼藤 貴志 大腿骨近位部骨折手術後の患者に対するTelerehabilitationの有効性 システマティック・レビューとメタアナリシス
Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain Research 2023.10 (一社)日本運動器疼痛学会
菊地 和人, 高沢浩太郎, 白土大成, 石光雄太 英国の産業理学療法ー本邦との比較・応用ー
第6回日本産業理学療法研究会学術大会 2023.10
白土大成 第56回 Global café 国際学会での発表経験の共有-事前準備と心構え- Invited
第56回 Global café 2025.3
白土大成 中小規模の調査研究を身近な環境で行うためのポイント Invited
日本老年療法学会 学術研修会 2025.8
白土大成 vol.12 なぜ20代で国立大学の助教に!?~アカデミアで働く理学療法士の本音~ 【プロの本音】 Invited
mMEDICI株式会社 2025.8
白土大成 地域在住高齢者へのリハビリテーション フレイルの社会的側面とその対策
リハオンデマンド 2025.12
白土大成 高齢期の理学療法に求められる評価視点と地域での実践
鹿児島県理学療法士協会 専門領域研修部 トピックス領域研修会 2025.2
白土大成 地域在住高齢者へのリハビリテーション 身体的フレイルとその対策
リハオンデマンド 2025.10
白土大成 地域在住高齢者へのリハビリテーション フレイルの精神、認知的側面とその対策
リハオンデマンド 2025.11
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 田平健人, 三宅悠斗 サルコペニア・フレイル対策における筋量・筋質・筋力と運動機能評価:現場での実践と意義
第12回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 2025.11
最優秀演題賞
2024.8 第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 地域在住高齢者における慢性疼痛がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響:睡眠の媒介効果
白土大成 , 牧迫 飛雄馬 , 赤井田 将真 , 立石 麻奈 , 木内 悠人 , 倉津 諒大 , 窪薗 琢郎 , 竹中 俊宏 , 桑波田 聡 , 大石 充
Top 100 ePoster abstract
2026.2 World Federation of Occupational Therapists 19th WFOT Congress 2026 Physical and Social Factors Differentiating Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Among Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Workers in Japan: A Cross-Sectional Study
Tamekuni Y., Okuyama K., Abe T., Motohiro A., Shiratsuchi D., Isomura M., Abrahamsson L., Lindström M., Sundquist K.
優秀演題賞(老年医学会部門・優秀ポスター)
2025.6 第34回日本老年学会総会 内在的能力は身体的フレイルの悪化および改善に寄与するか?―5年間の前向き研究―
牧迫飛雄馬, 白土大成, 三宅悠斗, 赤井田将真, 立石麻奈, 大塚礼, 窪薗琢郎, 竹中俊宏, 大石充
最優秀演題賞
2024.8 第3回日本老年療法学会学術集会 地域在住高齢者における慢性疼痛がフレイル状態の悪化に及ぼす影響:睡眠の媒介効果
白土大成, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 立石 麻奈, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 竹中 俊宏, 桑波田 聡, 大石 充
Top Downloaded Article
2024.3 GERIATRICS & GERONTOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Association of self-rated health with type and frequency of social interaction during the declaration of COVID-19 state of emergency among Japanese community-dwelling oldest-old adults
Shoma Akaida, Yuki Nakai, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kazutoshi Tomioka, Yoshiaki Taniguchi, Nana Sato, Ayumi Wada, Yuto Kiuchi, Saki Shono, Ryuhei Shiiba, Mana Tateishi, Hyuma Makizako
最優秀演題賞
2023.9 第2回日本老年療法学会学術集会 地域在住中高年者におけるCOVID-19流行禍の身体活動量の自己管理が3年後の身体機能に与える影響
立石 麻奈, 赤井田 将真, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 倉津 諒大, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 竹中 俊宏, 前田真由佳, 牧迫 飛雄馬
Top downloaded article
2023.3 Geriatrics & Gerontology International (Perceived declining physical and cognitive fitness during the COVID-19 state of emergency among community-dwelling Japanese old-old adults)
Hyuma Makizako, Yuki Nakai, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Tomomi Akanuma, Kaori Yokoyama, Yuriko Matsuzaki-Kihara, Hiroto Yoshida
Top cited article
2023.2 Geriatrics & Gerontology International (Perceived declining physical and cognitive fitness during the COVID-19 state of emergency among community-dwelling Japanese old-old adults)
Hyuma Makizako, Yuki Nakai, Daijo Shiratsuchi, Tomomi Akanuma, Kaori Yokoyama, Yuriko Matsuzaki-Kihara, Hiroto Yoshida
第9回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会 優秀演題賞
2022.10 自動車運転を中止した中高年者における交通の利用頻度と社会的フレイルの関連性, 第9回日本サルコペニア・フレイル学会大会
福榮竜也, 牧迫飛雄馬, 赤井田将真, 白土大成, 谷口善昭, 立石麻奈, 木内悠人, 愛下由香里, 倉津諒大
第1回日本老年療法学会学術集会 奨励賞
2022.10 地域在住高齢者におけるPGC-1α遺伝子多型と転倒との関連, 第1回日本老年療法学会学術集会
白土 大成, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 赤井田 将真, 窪薗 琢郎, 大石 充, 牧迫 飛雄馬
第64回日本老年医学会学術集会 会長奨励演題賞
2022.6 フレイル高齢者に対する個別運動と集団運動の介入効果の違い-ランダム化比較試験-, 第64回日本老年医学会学術集会
立石 麻奈, 牧迫 飛雄馬, 赤井田 将真, 生野 佐紀, 椎葉 竜平, 谷口 善昭, 木内 悠人, 白土 大成
第8回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会 奨励賞
2021.11 地域在住高齢者における前糖尿病および糖尿病と筋量、筋力、身体機能との関係, 第8回日本予防理学療法学会学術大会
椎葉 竜平, 中井 雄貴, 富岡 一俊, 谷口 善昭, 白土 大成, 木内 悠人, 竹中俊宏, 窪薗琢朗, 大石充, 牧迫 飛雄馬
World Physiotherapy Congress 2021 World Physiotherapy subgroup outstanding poster presentation award: International Federation of Physical Therapists working in Occupational Health and Ergonomics
2021.4 Association between presenteeism and low back pain among nurses in a Japanese acute care hospital: a cross-sectional study, World Physiotherapy Congress 2021
Daijo Shiratsuchi, Kosei Hashimoto, Norio Hamada, Kasumi Setaka, Daisuke Yoshida
通いの場参加行動に着目した高齢者の軽度認知障害に関するICT活用型疫学研究
2025.7 - 2026.3
Kagoshima University 令和7年度鹿児島大学地域活性化研究支援事業
社会参加における認知刺激とモチベーションに着目したMCI発症に関する疫学研究
Grant number:24K14249 2024.4 - 2028.3
日本学術振興会 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(C)
白土 大成
Authorship:Principal investigator
Grant amount:\4680000 ( Direct Cost: \3600000 、 Indirect Cost:\1080000 )
地域在住高年者における客観的睡眠状況と3年後のMCIおよびフレイルの発生との関連
Grant number:24K14141 2024.4 - 2028.3
日本学術振興会 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(C)
立石 麻奈
Authorship:Coinvestigator(s)
Grant amount:\4550000 ( Direct Cost: \3500000 、 Indirect Cost:\1050000 )
生活環境制御学
総合臨床実習Ⅱ
理学療法評価実習
症例研究法演習
総合臨床実習Ⅰ
身体機能評価学Ⅰ
身体機能評価学実習
身体機能評価学Ⅱ
チーム医療論Ⅱ
総合臨床実習Ⅱ
総合臨床実習Ⅰ
理学療法評価実習
理学療法学研究論
日々のストレッチでフレイルを予防 柔軟性の大切さを理学療法士に聞く Internet
Medical DOC https://medicaldoc.jp/m/column-m/202310t0182/ 2023.11
【フレイル予防】バランストレーニングで転倒を防ぐには? 理学療法士が解説 Internet
Medical DOC https://medicaldoc.jp/m/column-m/202310t0181/ 2023.11
「フレイル」と「骨粗しょう症」の関係とは フレイル予防が骨粗しょう症リスクを下げる? Internet
Medical DOC https://medicaldoc.jp/m/column-m/202310t0185/ 2023.11
Confirmation of the possibility that muscle weakness can be easily detected by the opening of plastic bottles. Internet
ITO EN, LTD. 伊藤園ニュースリリース https://www.itoen.co.jp/news/article/57372/ 2023.10
ペットボトルの開け方で筋力把握、「逆筒握り」は筋力低下のサインに/伊藤園が鹿児島大学医学部と共同研究 Internet
YAHOO! JAPAN ニュース https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/fe260868262c48d9d48f634c0165f6fdd9e38cfa 2023.10
健康情報を使いこなすためのヘルスリテラシー入門編 Internet
LIFit https://arce-lifit.com/2021/08/13/health_literacy/ 2021.8
健康情報を使いこなすためのヘルスリテラシー続編 Internet
LIFit https://arce-lifit.com/2021/08/27/health_literacy_sequel/ 2021.8
コロナ禍で体力の衰えを感じた人は活動量が低下している? Internet
LIFit https://arce-lifit.com/2021/05/14/covid-19_activity/ 2021.5
震災から学ぶ適切なソーシャルディスタンス Internet
LIFit https://arce-lifit.com/2021/03/11/%e9%9c%87%e7%81%bd%e3%81%8b%e3%82%89%e5%ad%a6%e3%81%b6%e9%81%a9%e5%88%87%e3%81%aa%e3%82%bd%e3%83%bc%e3%82%b7%e3%83%a3%e3%83%ab%e3%83%87%e3%82%a3%e3%82%b9%e3%82%bf%e3%83%b3%e3%82%b9/ 2021.4
社会的な繋がりの欠如はフレイルドミノの始まり!? Internet
LIFit https://arce-lifit.com/2020/04/25/flaildomino-society/ 2021.2
BMC Geriatrics
Role(s): Peer review
2024.4
The Gerontologist
Role(s): Peer review
2024.4
Psychogeriatrics
Role(s): Peer review
2024.4
Lipids in Health and Disease
Role(s): Peer review
2024.4
Journal of Japanese Association on Sarcopenia and Frailty
Role(s): Peer review
2024.3
The Gerontologist
Role(s): Peer review
2024.3
Geriatrics & Gerontology International
Role(s): Peer review
2024.2
Journal of Physical Therapy for Prevention
Role(s): Peer review
2024.1 - 2024.3
理学療法かごしま
Role(s): Peer review
2023.12 - 2024.3
理学療法かごしま
Role(s): Peer review
2023.9 - 2023.11
Scientific Reports
Role(s): Peer review
2023.8 - 2023.12